# Trabalho prático 5 - RIP
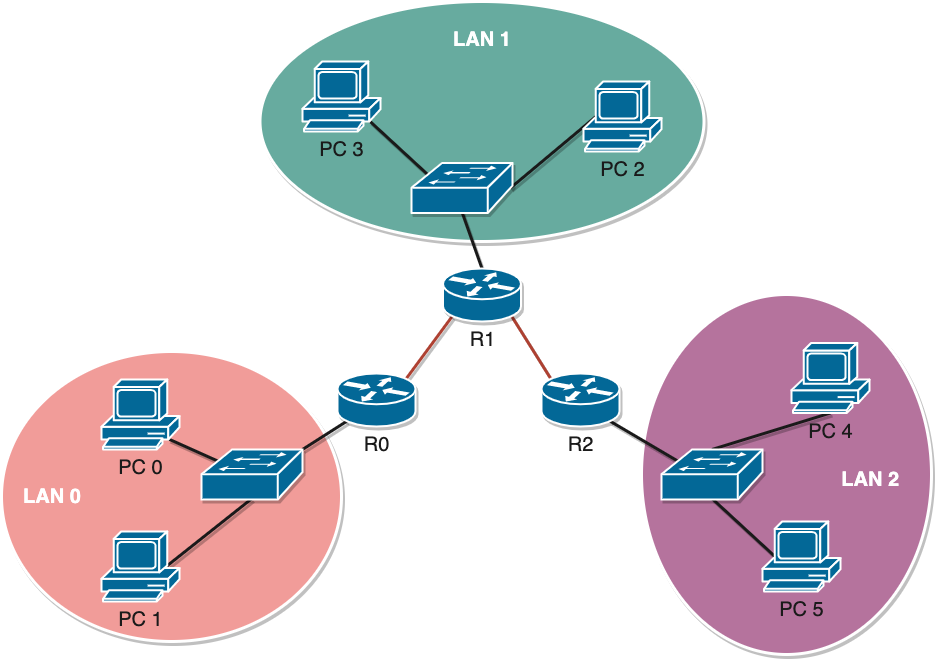
# Considere o seguinte cenário de rede:
Baixar arquivo - packet tracer
Considere que dispõe da rede 172.16.0.0/16 para atribuir às redes locais e a rede 10.0.0.0/24 para atribuir à ligações entre os routers. Cada uma das redes locais deverá suportar 200 hosts ligados.
# Defina as redes que vai usar
- Rede 0: 172.16.0.0/24
- Rede 1: 172.16.1.0/24
- Rede 2: 172.16.2.0/24
- Router 0
- Router 1
- Router 0
# Primeira implementação
# Apague as configurações do router.
Igual para todos os routers
Router> enable
Router# erase startup-config
Router# reload
# Liste as interfaces do router.
Comando é igual para todos
Router# show ip interface brief
O resultado pode variar de router para router
# Resultado:
Interface IP-Address OK? Method Status Protocol
FastEthernet0/0 unassigned YES NVRAM administratively down down
FastEthernet0/1 unassigned YES NVRAM administratively down down
Serial0/0/0 unassigned YES NVRAM administratively down down
Serial0/0/1 unassigned YES NVRAM administratively down down
Vlan1 unassigned YES NVRAM administratively down down
# Entre em modo de configuração. Altere o nome do router para R0.
O Comando é o mesmo para o três routers
Router R0 como exemplo
Router# configure terminal
Router(config)# hostname R0
R0(config)#
# Configure a Interfaces FastEthernet e as Interfaces Serial
# Router R0
R0(config)# interface fastEthernet 0/0
R0(config-if)# ip address 172.16.0.254 255.255.255.0
R0(config-if)# no shutdown
R0(config-if)# exit
R0(config)# interface serial 0/0/0
R0(config-if)# ip address 10.0.0.1 255.255.255.252
R0(config-if)# clock rate 64000
R0(config-if)# no shutdown
# Router R1
R1(config)# interface fastEthernet 0/0
R1(config-if)# ip address 172.16.1.254 255.255.255.0
R1(config-if)# no shutdown
R1(config-if)# exit
R1(config)# interface serial 0/0/0
R1(config-if)# ip address 10.0.0.2 255.255.255.252
R1(config-if)# no shutdown
R1(config-if)# exit
R1(config)# interface Serial 0/0/1
R1(config-if)# ip address 10.0.0.5 255.255.255.252
R1(config-if)# clock rate 64000
R1(config-if)# no shutdown
# Router R2
R2(config)# interface fastEthernet 0/0
R2(config-if)# ip address 172.16.2.254 255.255.255.0
R2(config-if)# no shutdown
R2(config-if)# exit
R2(config)# interface serial 0/0/0
R2(config-if)# ip address 10.0.0.6 255.255.255.252
R2(config-if)# no shutdown
# Ative o RIP versão 2 e adicione as redes ligadas às interfaces do tipo Serial e FastEthernet. Coloque as interfaces FastEthernet em modo passivo. Qual é a finalidade deste comando?
# Router R0
R0(config)# router rip
R0(config-router)# version 2
R0(config-router)# network 172.16.0.0
R0(config-router)# network 10.0.0.0
R0(config-router)# passive-interface fastEthernet 0/0
# Router R1
R1(config)# router rip
R1(config-router)# version 2
R1(config-router)# network 172.16.1.0
R1(config-router)# network 10.0.0.0
R1(config-router)# network 10.0.0.4
R1(config-router)# passive-interface fastEthernet 0/0
# Router R2
R2(config-if)# router rip
R2(config-router)# version 2
R2(config-router)# network 172.16.2.0
R2(config-router)# network 10.0.0.4
R2(config-router)# passive-interface fastEthernet 0/0
# Passive Interface
O comando passive-interface quando aplicado a uma interface do router impede que sejam enviados pacotes RIP por essa interface, e assim, impede que o router anuncie rotas através dessa interface.
# Confirme quais as rotas conhecidas pelos routers e analise as métrica de routing apresentada para cada rota.
# Router R0
R0# show ip route
# Resultado:
10.0.0.0/30 is subnetted, 2 subnets
C 10.0.0.0 is directly connected, Serial0/0/0
R 10.0.0.4 [120/1] via 10.0.0.2, 00:00:23, Serial0/0/0
172.16.0.0/16 is variably subnetted, 2 subnets, 2 masks
R 172.16.0.0/16 [120/1] via 10.0.0.2, 00:00:23, Serial0/0/0
C 172.16.0.0/24 is directly connected, FastEthernet0/0
# Router R1
R1# show ip route
# Resultado:
10.0.0.0/30 is subnetted, 2 subnets
C 10.0.0.0 is directly connected, Serial0/0/0
C 10.0.0.4 is directly connected, Serial0/0/1
172.16.0.0/16 is variably subnetted, 2 subnets, 2 masks
R 172.16.0.0/16 [120/1] via 10.0.0.6, 00:00:21, Serial0/0/1
[120/1] via 10.0.0.1, 00:00:06, Serial0/0/0
C 172.16.1.0/24 is directly connected, FastEthernet0/0
# Router R2
R2# show ip route
# Resultado:
10.0.0.0/30 is subnetted, 2 subnets
R 10.0.0.0 [120/1] via 10.0.0.5, 00:00:16, Serial0/0/0
C 10.0.0.4 is directly connected, Serial0/0/0
172.16.0.0/16 is variably subnetted, 2 subnets, 2 masks
R 172.16.0.0/16 [120/1] via 10.0.0.5, 00:00:16, Serial0/0/0
C 172.16.2.0/24 is directly connected, FastEthernet0/0
# Configure no Router 1 o RIP para anunciar a rota por defeito. Anote as diferenças registadas nas tabelas e routing dos routers R0 e R2.
# Configuração do R1
R1> enable
R1# configure terminal
R1(config)# router rip
R1(config-router)# default-information originate
R1(config-router)# end
R1# show ip route
# Resultado:
10.0.0.0/30 is subnetted, 2 subnets
C 10.0.0.0 is directly connected, Serial0/0/0
C 10.0.0.4 is directly connected, Serial0/0/1
172.16.0.0/16 is variably subnetted, 2 subnets, 2 masks
R 172.16.0.0/16 [120/1] via 10.0.0.6, 00:00:12, Serial0/0/1
[120/1] via 10.0.0.1, 00:00:06, Serial0/0/0
C 172.16.1.0/24 is directly connected, FastEthernet0/0
# Diferenças registadas nas tabelas e routing dos routers R0 e R2
# Router R0
R0# show ip route
# Resultado:
Gateway of last resort is 10.0.0.2 to network 0.0.0.0
10.0.0.0/30 is subnetted, 2 subnets
C 10.0.0.0 is directly connected, Serial0/0/0
R 10.0.0.4 [120/1] via 10.0.0.2, 00:00:22, Serial0/0/0
172.16.0.0/16 is variably subnetted, 2 subnets, 2 masks
R 172.16.0.0/16 [120/1] via 10.0.0.2, 00:00:22, Serial0/0/0
C 172.16.0.0/24 is directly connected, FastEthernet0/0
R* 0.0.0.0/0 [120/1] via 10.0.0.2, 00:00:10, Serial0/0/0
# Router R2
R2> show ip route
# Resultado:
Gateway of last resort is 10.0.0.5 to network 0.0.0.0
10.0.0.0/30 is subnetted, 2 subnets
R 10.0.0.0 [120/1] via 10.0.0.5, 00:00:00, Serial0/0/0
C 10.0.0.4 is directly connected, Serial0/0/0
172.16.0.0/16 is variably subnetted, 2 subnets, 2 masks
R 172.16.0.0/16 [120/1] via 10.0.0.5, 00:00:00, Serial0/0/0
C 172.16.2.0/24 is directly connected, FastEthernet0/0
R* 0.0.0.0/0 [120/1] via 10.0.0.5, 00:00:00, Serial0/0/0
Ao definir o R1 como router padrão, R1 passa a ser o router que liga ao "qualquer lado", será usado sempre que for necessário comunicar com um host de uma rede não "conhecida" / declarada. Como consequência da nossa declaração, as tabelas de routing de R0 e R2 foram atualizadas pelo RIP com a informação da rota padrão.
# Analise a saída do comando "show ip protocols"
R1 como exemplo
R1> show ip protocols
# Resultado:
Routing Protocol is "rip"
Sending updates every 30 seconds, next due in 26 seconds
Invalid after 180 seconds, hold down 180, flushed after 240
Outgoing update filter list for all interfaces is not set
Incoming update filter list for all interfaces is not set
Redistributing: rip
Default version control: send version 2, receive 2
Interface Send Recv Triggered RIP Key-chain
Serial0/0/0 2 2
Serial0/0/1 2 2
Automatic network summarization is in effect
Maximum path: 4
Routing for Networks:
10.0.0.0
172.16.0.0
Passive Interface(s):
FastEthernet0/0
Routing Information Sources:
Gateway Distance Last Update
10.0.0.6 120 00:00:15
10.0.0.1 120 00:00:09
Distance: (default is 120)
O comando show ip protocols mostra todos os protocolos de encaminhamento configurados no router.
O comando apresenta os valores dos temporizadores, as redes diretamente ligadas ao router e os endereços das interfaces dos routers vizinhos a que está ligado.
Protocolos em uso: RIP, versão (send and receive): 2 são a mesma para todas a interfaces
Suas redes: 10.0.0.0; 172.16.0.0
passive interfaces : FastEthernet 0/0
Interfaces dos routers vizinhos: 10.0.0.6 - 120; 10.0.0.1 - 120120 á a distancia administrativa padrão usada pelo RIP
Default Administrative Distance (opens new window)
# Confirme quais as rotas conhecidas pelo routers
Usar o comando show ip route para saber todas as rotas ou show ip route rip para saber só as definidas pelo RIP.
# Router R0 (todas)
10.0.0.0/30 is subnetted, 2 subnets
C 10.0.0.0 is directly connected, Serial0/0/0
R 10.0.0.4 [120/1] via 10.0.0.2, 00:00:19, Serial0/0/0
172.16.0.0/16 is variably subnetted, 2 subnets, 2 masks
R 172.16.0.0/16 [120/1] via 10.0.0.2, 00:00:19, Serial0/0/0
C 172.16.0.0/24 is directly connected, FastEthernet0/0
R* 0.0.0.0/0 [120/1] via 10.0.0.2, 00:00:19, Serial0/0/0
# Router R1 (todas)
10.0.0.0/30 is subnetted, 2 subnets
C 10.0.0.0 is directly connected, Serial0/0/0
C 10.0.0.4 is directly connected, Serial0/0/1
172.16.0.0/16 is variably subnetted, 2 subnets, 2 masks
R 172.16.0.0/16 [120/1] via 10.0.0.6, 00:00:06, Serial0/0/1
[120/1] via 10.0.0.1, 00:00:08, Serial0/0/0
C 172.16.1.0/24 is directly connected, FastEthernet0/0
# Router R2 (só RIP)
10.0.0.0/30 is subnetted, 2 subnets
R 10.0.0.0 [120/1] via 10.0.0.5, 00:00:14, Serial0/0/0
172.16.0.0/16 is variably subnetted, 2 subnets, 2 masks
R 172.16.0.0/16 [120/1] via 10.0.0.5, 00:00:14, Serial0/0/0
R* 0.0.0.0/0 [120/1] via 10.0.0.5, 00:00:14, Serial0/0/0
# Grave a configuração
Pode-se usar o comando copy running-config startup-config (copy run start) ou write memory (wr).
Difference between "copy run start" and wr (opens new window)
# Verifique a conectividade entre redes utilizando o comando ping
Abrir a linha de comandos (terminal, prompt, cmd, power shell,...) e executar o comando ping _ip destino_ pode ver exemplos do mesmo comando nos protocolos anteriores.
# Verifique qual o seguido pelos pacotes utilizando o comando traceroute
Como exemplo PC0
C:\> tracert 172.16.2.2
# Resultado:
Tracing route to 172.16.2.2 over a maximum of 30 hops:
1 * 0 ms 5 ms 172.16.0.254
2 * 0 ms * Request timed out.
3 56 ms 1 ms 1 ms 10.0.0.6
4 * * * Request timed out.
5 2 ms 2 ms 0 ms 172.16.2.2
Trace complete.
# Segunda implementação
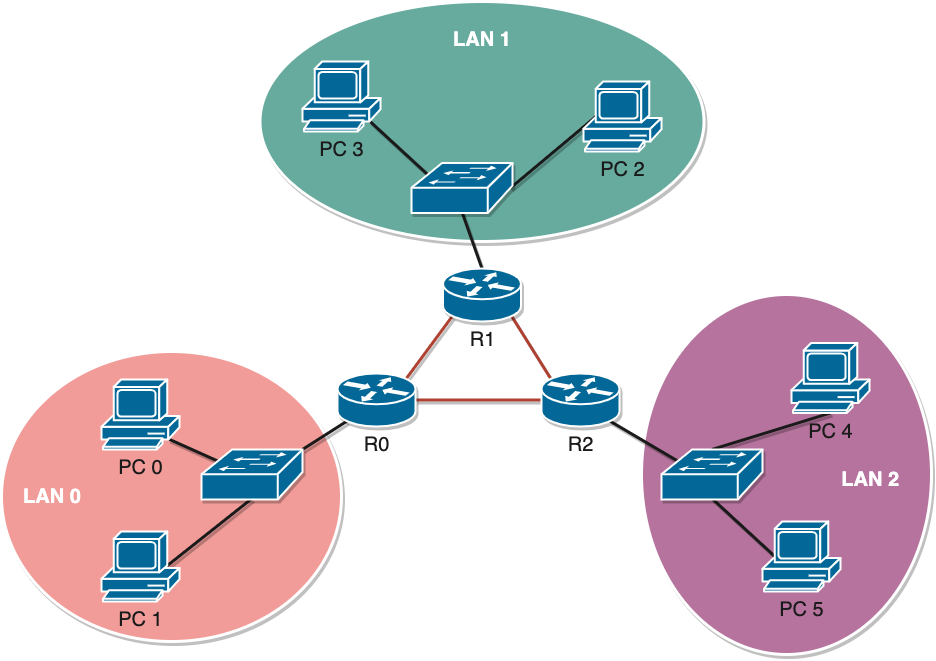
# Repita o exercício anterior para o seguinte cenário
# Configura as interfaces
# Router R0
R0> enable
R0# configure terminal
R0(config)# interface serial 0/0/1
R0(config-if)# ip address 10.0.0.9 255.255.255.252
R0(config-if)# clock rate 64000
R0(config-if)# no shutdown
R0(config-if)# end
# Router R2
R2> enable
R2# configure terminal
R2(config)# interface serial 0/0/1
R2(config-if)# ip address 10.0.0.10 255.255.255.252
R2(config-if)# no shutdown
R2(config-if)# end
# Configurar o RIP
# Router R0
R0# configure terminal
R0(config)# router rip
R0(config-router)# network 10.0.0.8
R0(config-router)# end
# Router R2
R2# configure terminal
R2(config)# router rip
R2(config-router)# network 10.0.0.8
R2(config-router)# end
# Analise a saída do comando show ip protocols
# Router R0
R0# show ip protocols
# Resultado:
Routing Protocol is "rip"
Sending updates every 30 seconds, next due in 8 seconds
Invalid after 180 seconds, hold down 180, flushed after 240
Outgoing update filter list for all interfaces is not set
Incoming update filter list for all interfaces is not set
Redistributing: rip
Default version control: send version 2, receive 2
Interface Send Recv Triggered RIP Key-chain
Serial0/0/0 2 2
Serial0/0/1 2 2
Automatic network summarization is in effect
Maximum path: 4
Routing for Networks:
10.0.0.0
172.16.0.0
Passive Interface(s):
FastEthernet0/0
Routing Information Sources:
Gateway Distance Last Update
10.0.0.2 120 00:00:16
10.0.0.10 120 00:00:03
Distance: (default is 120)
# Router R2
R2# show ip protocols
# Resultado:
Routing Protocol is "rip"
Sending updates every 30 seconds, next due in 1 seconds
Invalid after 180 seconds, hold down 180, flushed after 240
Outgoing update filter list for all interfaces is not set
Incoming update filter list for all interfaces is not set
Redistributing: rip
Default version control: send version 2, receive 2
Interface Send Recv Triggered RIP Key-chain
FastEthernet0/0 2 2
Serial0/0/0 2 2
Serial0/0/1 2 2
Automatic network summarization is in effect
Maximum path: 4
Routing for Networks:
10.0.0.0
172.16.0.0
Passive Interface(s):
Routing Information Sources:
Gateway Distance Last Update
10.0.0.5 120 00:00:10
10.0.0.9 120 00:00:14
Distance: (default is 120)
A rota de Router R0
Router R2 passou a ser pelo o ip gateway 10.0.0.10e a rota de Router R2Router R0 passou a ser pelo o ip gateway 10.0.0.9
# Confirme as rotas conhecidas pelos routers
Router R0 como exemplo
R0>show ip route
# Resultado:
10.0.0.0/30 is subnetted, 3 subnets
C 10.0.0.0 is directly connected, Serial0/0/0
R 10.0.0.4 [120/1] via 10.0.0.2, 00:00:24, Serial0/0/0
[120/1] via 10.0.0.10, 00:00:25, Serial0/0/1
C 10.0.0.8 is directly connected, Serial0/0/1
172.16.0.0/16 is variably subnetted, 2 subnets, 2 masks
R 172.16.0.0/16 [120/1] via 10.0.0.2, 00:00:24, Serial0/0/0
C 172.16.0.0/24 is directly connected, FastEthernet0/0
R* 0.0.0.0/0 [120/1] via 10.0.0.2, 00:00:24, Serial0/0/0
# Verifique a conetividade entre as redes utilizando o comando ping.
PC0
C:\> ping 172.16.2.2
Pinging 172.16.1.1 with 32 bytes of data:
Pinging 172.16.2.2 with 32 bytes of data:
Reply from 172.16.2.2: bytes=32 time=2ms TTL=126
Reply from 172.16.2.2: bytes=32 time=60ms TTL=126
Reply from 172.16.2.2: bytes=32 time=1ms TTL=126
Reply from 172.16.2.2: bytes=32 time=61ms TTL=126
Ping statistics for 172.16.2.2:
Packets: Sent = 4, Received = 4, Lost = 0 (0% loss),
Approximate round trip times in milli-seconds:
Minimum = 1ms, Maximum = 61ms, Average = 31ms
# Verifique qual o caminho seguido pelos pacotes utilizando o comando traceroute.
PC0
C:\>tracert 172.16.2.2
# Resultado
Tracing route to 172.16.2.2 over a maximum of 30 hops:
1 76 ms 0 ms 0 ms 172.16.0.254
2 * 0 ms 0 ms 10.0.0.2
3 0 ms 1 ms 0 ms 172.16.0.254
4 1 ms 1 ms 0 ms 10.0.0.2
5 1 ms 1 ms 62 ms 172.16.0.254
6 0 ms 3 ms 0 ms 10.0.0.2
7 3 ms 2 ms 177 ms 172.16.0.254
8 4 ms 126 ms 2 ms 10.0.0.2
9 2 ms 2 ms 3 ms 172.16.0.254
10 1 ms 0 ms 168 ms 10.0.0.2
11 107 ms 169 ms 1 ms 172.16.0.254
12 159 ms 213 ms 5 ms 10.0.0.2
13 3 ms 3 ms 6 ms 172.16.0.254
14 206 ms 2 ms 2 ms 10.0.0.2
15 1 ms 170 ms 592 ms 172.16.0.254
16 5 ms 3 ms 65 ms 10.0.0.2
17 2 ms 64 ms 2 ms 172.16.0.254
18 371 ms 392 ms 63 ms 10.0.0.2
19 1 ms 5 ms 4 ms 172.16.0.254
20 4 ms 3 ms 220 ms 10.0.0.2
21 4 ms 125 ms 113 ms 172.16.0.254
22 115 ms 4 ms 1 ms 172.16.2.2